Filtering
Filtering is a way to exclude data you do not want to see or use in your analysis. Because less data gets loaded, filtering also reduces the processing times for queries so you can work faster.
When writing queries, filtering is accomplished using the where method and other related methods described below. There are two categories of filters in Deephaven: Match filters and Conditional filters.
If a filter operation is the cause of a failed query, the exception in the Deephaven interface will prompt you to clear filters with the accompanying Clear Filtering button or access to the right-click menu.
where()
Syntax
where("USym = `AAPL`)
The where method returns all the rows from the source table that meet the conditions in the argument.
For example:
t = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("USym = `AAPL`")
You could also write this like:
t = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`", "USym = `AAPL`")
Filters are applied from left to right. Therefore, the order in which they are passed to the function can have a substantial impact on the execution time.
For example, if we moved the "USym" filter first, Deephaven would evaluate that filter for all partitions of the table before reducing the data to a single date.
t = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("USym = `AAPL`", "Date = `2017-08-25`")
In this case, you won't see much of a difference because these examples use relatively small tables. However, when your table size grows to thousands or millions of rows (or more), you will want to ensure you are filtering the data in the most efficient method to reduce compute expense and execution time.
Partitioning and Grouping Columns
When you partition a hard drive, you are dividing the entire hard drive into multiple, logical, independent volumes. In a high-end data system like Deephaven, data is also divided into multiple, logical and independent partitions, which improves the speed, performance and efficiency of the data analysis.
For example, if a dataset includes information about every cell phone call made in a given city over 10 years, a logical way to partition that data would be by a date range. Instead of having one massive file that contained every record for that time period, 10 smaller partitions could be created to hold the data related to one year of calls. If data was needed to analyze only a specific range of time, the entire data set would not need to be analyzed again. Rather, the analysis could be performed on one or more of the smaller partitions, which would take considerably less time.
The Deephaven query language is designed to make filtering on partitioning columns highly efficient. Therefore, when possible, one should filter first on partitioning columns.
Grouping columns determine how table data is organized on disk such that each unique value, and its related row data, are located in contiguous blocks of rows. These have persistent indexes that the Deephaven query engine can leverage to vastly improve the efficiency of match filters.
If your analyses require filtering on the data contained in both partitioning columns and grouping columns, the most efficient method would be to first filter on partitioning columns, and then separately filter on grouping columns and/or any remaining columns as needed.
To determine the partitioning and grouping columns in your dataset, you will need to review the metadata for your applicable table(s). One way this can be accomplished is by using the getMeta method, which will return a table with column details.
tMeta=db.t("<namespace>", "<tablename>").getMeta()
Match Filters
The previous example used match filters. Because match filters benefit from special handling in Deephaven, you should use them whenever possible and before any conditional filters. Match filters often enable Deephaven to perform optimizations that would not be possible with a potentially more expressive conditional filter. For example, grouping information on historical data sources can be used with match filters, but not conditional filters.
There are five kinds of match filters in Deephaven:
=(the equal sign)innot inicase inicase not in
Note: match filters must be used individually. They cannot be combined in the same filter string with other match filters or conditional filters.
= (the equal sign)
Syntax
.where("columnName=value")
This method returns rows that have a matching value in the specified column.
Example
The following filter returns rows where the value of "child" is included in the column Age.
t = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`", "USym = `AAPL`")
in
Syntax
.where("columnName in valueList")
This method returns rows that contain a match of one or more values in the specified column.
Example
t = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("USym in `AAPL` , `GOOG`")
not in
Syntax
.where("columnName not in valueList")
This method returns rows that do not contain a match of one or more values in the specified column.
Example
t = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("USym not in `AAPL` , `GOOG`")
icase in
Syntax
.where("columnName icase in valueList")
This method returns rows that contain a match of one or more values in the specified column regardless of the capitalization of the values.
Example
t = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("USym icase in `aapl` , `goog`")
icase not in
Syntax
.where("columnName icase not in valueList")
This method returns rows that do not contain a match of one or more values in the specified column regardless of the capitalization of the values.
Example
t = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("USym icase not in `aapl` , `goog`")
Using Variables within Match Filters
The right side of a match filter using the "in" statement allows for use of variables as follows:
- list of variables:
AinX,Y,Z- the filter will return true for all the rows whereAis equal toX,YorZ - single variable name:
AinX:- If
Xis a Java array orjava.util.Collection, the filter will return true for all the rows whereAis equal to one element ofX - For all other types of
X, the filter will return true for all the rows whereAis equal toX
- If
Conversely, the right side of a not in statement allows for use of variables as follows:
- list of variables:
Anot inX,Y,Z- the filter will return true for all the rows whereAis not equal toX,YorZ - single variable name
Anot inX:- If
Xis a Java array or Collection, the filter will return true for all the rows whereAis not equal to one element ofX - For all other types of
X, the filter will return true for all the rows whereAis not equal toX
- If
Conditional Filters
Conditional filters can be used to filter data based on formulas other than those included in match filters. Conditional filters are not optimized like match filters. Therefore they should be placed after match filters in a given where clause. Conditional filters can be any arbitrary Java expression evaluator, including:
where.("x==y")where("x>y")where("x<y")startsWith()endsWith()
Note that match filters and conditional filters cannot be used together in the same filter string.
Examples of conditional filters follow:
Example
t2 = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("Bid>30")
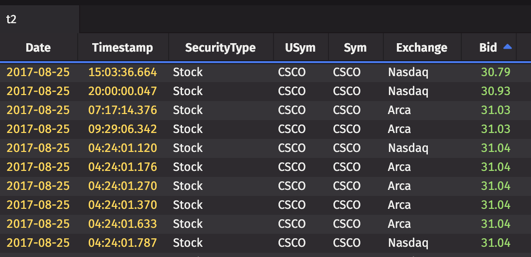
As you can see below, the lowest value in t2 is now 30.79.
Example
t3 = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("Bid%2==0")
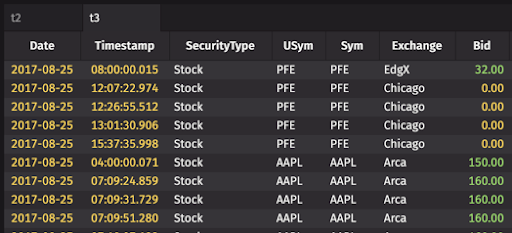
In t3 , the filter returns rows only if the value in the Bid column is exactly divisible by 2.
Example
The next example uses formulas on multiple columns.
t4 = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("BidSize%2==1","Exchange.startsWith(`N`)")
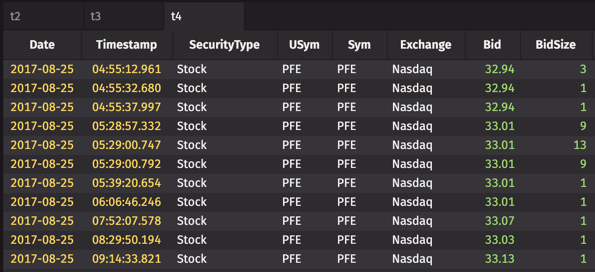
Here, StockQuotes is filtered to rows where:
- the value in the BidSize column has a remainder of 1 after being divided by 2, and
- the value in the Exchange column starts with the string
N.
Note: Because this is Java code, all the normal constraints of Java code must be respected. For example, in the filter "C.startsWith(`AA`)", the variable C, may not be NULL otherwise a NullPointerException will result. You must keep your condition filter code consistent with your data. If you expect NULL values, you must first check for null values (e.g., "C != null && C.startsWith(`AA`)").
Conjunctive and Disjunctive Filtering
When filtering on multiple columns in a table, your query can be written so they work on a conjunctive basis or a disjunctive basis.
Conjunctive
In conjunctive filtering, all filters within a where() clause are evaluated. For example, two filters are working conjunctively in the following:
t5 = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("Bid>30","Exchange.startsWith(`N`)")
In this case, the filter returns rows only when the value in the Bid column is greater than 25, and the value in the Exchange column starts with the string N.
The following sample queries all use equivalent variations of conjunctive filtering
t2=t1.where("A in firstSet", "B in secondSet")
Assuming firstSet and secondSet are collections, this could also be written with a condition filter as:
t3=t1.where("firstSet.contains(A)", "secondSet.contains(B)")
or even:
t4=t1.where("firstSet.contains(A) && secondSet.contains(B)")
t2 will evaluate, using an optimized match filter, "A in firstSet" and then only for values which match the A filter, it will evaluate "B in secondSet".
t3 is logically the same, but instead of using an optimized match filter, it will evaluate the A column for each row and pass it to the condition filter "firstSet.contains(A)". For rows that pass this filter, it will evaluate the B column, and pass those values to "secondSet.contains(B)".
t4 will produce the same output as t3, but the A and B columns are evaluated and passed into the filter expression ("firstSet.contains(A) && secondSet.contains(B)").
Disjunctive
In disjunctive filtering, each filter clause is evaluated independently, and results are presented if any of the filters return results.
For example, two filters are working disjunctively in this clause:
t6 = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
.where("Bid>30 || Exchange.startsWith(`N`)")
In this case, the filter will present rows only when the value in the Bid column is greater than 30, or the value in the Exchange column starts with the string N, or both.
The following syntax can also be used to indicate disjunctive filtering:
.whereOneOf("Bid>25", "Exchange.startsWith(`N`)")
Composing Complex Where Clauses
When building a query that applies multiple filters to the same data, the best approach is to chain multiple filter clauses within the same where method.
When you use any filter on a partitioning column or when you specifically use a match filter on a grouping column, that filter should be an independent clause.
If you have a complex formula, then it is best to combine the clauses if and only if they reference the same column(s).
Multiple clauses can be combined into single where method calls or separated into multiple where method calls. The results and processing effort are the same, but multiple where clauses may improve readability of the query.
Order matters and you should generally put the more selective or more efficient filters first, although the exact performance may vary depending on the filters themselves or the data being filtered. In many cases, doing so allows the query engine to avoid overhead.
The following where clauses illustrate these differences:
|
Quality |
Query |
Discussion |
|---|---|---|
|
Good |
|
The partitioning column ( |
|
Bad |
|
The |
|
Bad |
|
The partitioning column ( |
|
Good |
|
The partitioning column ( |
|
Less Good |
|
The partitioning column ( |
|
Less Good |
|
The partitioning column ( |
|
Good |
|
The partitioning column ( |
|
Bad |
|
The partitioning column ( |
whereIn and whereNotIn
The whereIn and whereNotIn methods enable you to filter one table based on the contents of another table, which may or may not contain ticking data.
A where clause is evaluated only when a row in the filtered table ticks. whereIn and whereNotIn are evaluated whenever either table changes. Join expressions, such as join and naturalJoin are also evaluated when either table changes.
The syntax follows:
validResults = tableToFilter.whereIn(validValuesTable, "ColName")
The tableToFilter is the left table; the validValuesTable table is the right table. This query will filter the specified column in tableToFilter to only the values in the validValueTables and store the results in a new table, validResults.
The whereNotIn syntax is identical:
invalidResults = tableToFilter.whereNotIn(validValuesTable, "ColName")
As you can imagine, returns the values from the specified column that do not appear in our validValuesTable, or the "invalid" results.
You can also specify more than one column to filter, and the names need not be the same.
For example, if we wanted to match on USym and Expiry, but the tableToFilter table had a column named Maturity instead, we could use the following construct:
validResults=tableToFilter.whereIn(validValueTables, "USym", "Maturity=Expiry")
whereIn is not appropriate for all situations. Its purpose is to enable more efficient filtering for a set that changes infrequently. Any time the right table (in this example validValuesTable) ticks, all rows of the left table (tableToFilter) must be re-evaluated. If you have a right table that often ticks, you should use a naturalJoin instead.
Example
To demonstrate, we will create a usymsOfInterest table. If this were a ticking table, its contents could vary as it returns the first three distinct USyms at any given time. Then, we'll filter another table of stock data (that might include thousands of USyms), to only show the USyms that we care about — the ones in your usymsOfInterest table. We'll also create table with the invalid results.
trades = db.t("LearnDeephaven", "StockTrades").where("Date=`2017-08-25`")
usymsOfInterest = trades.countBy("Count", "USym").sortDescending("Count").head(3)
interestingStockQuotes = trades.whereIn(usymsOfInterest, "USym")
invalid=trades.whereNotIn(usymsOfInterest, "USym")
trades = db.t("LearnDeephaven", "StockTrades").where("Date=`2017-08-25`")
usymsOfInterest = trades.countBy("Count", "USym").sortDescending(“Count”).head(3)
interestingStockQuotes = trades.whereIn(usymsOfInterest, "USym")
invalid=trades.whereNotIn(usymsOfInterest, "USym")
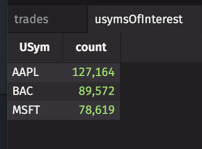
In the image below, we used the Advanced Filters dialog as a quick way to confirm interestingStockQuotes is limited to three USyms in our usymsOfInterest table.
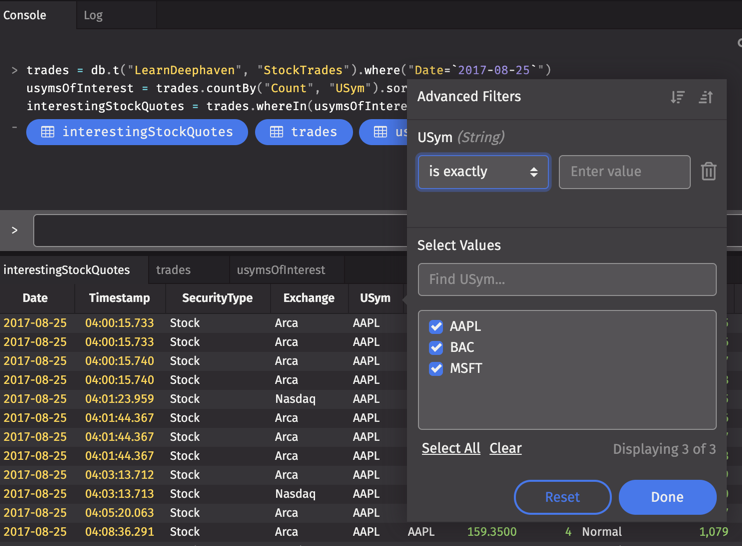
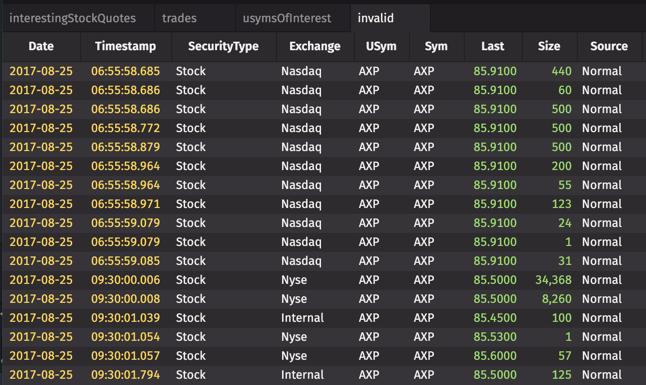
The invalid table contains only rows with a USym value that is not in the usymsOfInterest list.
Unlike naturalJoin, whereIn can be used when there are more than one matching value in the right table for values in the left table. This is true of join as well, but whereIn is faster to return matching rows than join.
Also, whereIn only provides filtering, and does not allow adding columns from the right table. In some cases it may be desirable to use whereIn to filter and then join to add columns from the right table. This provides similar performance to naturalJoin while still allowing multiple matches from the right table.
See also When to use whereIn or naturalJoin?
Head & Tail Filtering
Head and tail filters are used to return the first or last set of rows of a table by specifying the number of rows desired or by specifying the percent of the table. See also: Dedicated Aggregators.
The following filters are used to return a specific number of rows:
head()tail()
The following filters are used to return a specific percentage of rows:
headPct()tailPct()
For example,
t = db.t("LearnDeephaven" , "StockQuotes")\
.where("Date = `2017-08-25`")\
t2 = t.head(10) // returns the first 10 rows of a table
t3 = t.tail(20) // returns the last 20 rows of a table
t4 = t.headPct(0.25) // returns the first 25% of rows contained in a table
t5 = t.tailPct(0.5) // returns the last 50% of rows contained in a table
DownsampledWhereFilter
The DownsampledWhereFilter enables users to downsample time series data by calculating the bin intervals for values, and then using upperBin and lastBy to select the last row for each bin. Note: The column containing the data to be binned must be sorted for the method to work. A sample query using this method follows:
from deephaven import *
downsampledX = x.where(DownsampledWhereFilter("Timestamp", 5*dbtu.MINUTE))
import com.illumon.iris.db.v2.select.DownsampledWhereFilter
downsampledX = x.where(new DownsampledWhereFilter("Timestamp", 5 * MINUTE))
The default for this method is to downsample the bins based on upperBin and lastBy. However, you can downsample the bin based on lowerBin and firstBy by adding a third argument to the DownsampledWhereFilter method. An example follows with the third argument highlighted:
from deephaven import *
downsampledX = x.where(DownsampledWhereFilter("Timestamp", 5*dbtu.MINUTE,
DownsampledWhereFilter.SampleOrder.LOWERFIRST))
import com.illumon.iris.db.v2.select.DownsampledWhereFilter
downsampledX = x.where(new DownsampledWhereFilter("Timestamp", 5 * MINUTE,
DownsampledWhereFilter.SampleOrder.LOWERFIRST))
LOWERFIRST is the constant for lowerBin/firstBy.
UPPERLAST is the constant for upperBin/lastBy.
Either constant works in this query. However, if the third argument is not present, the downsampling will occur on an upperBin/lastBy basis.
Note: The DownsampleWhereFilter cannot be used on ticking tables. To use it against intraday data, one option would be use false as a third argument for db.i(); e.g., p=db.i("DbInternal","ProcessEventLog",false).where("Date=currentDateNy()").
Examples
All the following examples will give you the same result of trades after or including 11am:
p=db.i("SystemEquity","TradeData").where("Date=`2012-02-15`", "Timestamp>='2012-02-15T11:00:00 NY'")
p=db.i("SystemEquity","TradeData").where("Date=`2012-02-15`", "Timestamp+'1:00:00'>='2012-02-15T10:00:00 NY'")
p=db.i("SystemEquity","TradeData").where("Date=`2012-02-15`", "Timestamp+'T1h'>='2012-02-15T10:00:00 NY'")
p=db.i("SystemEquity","TradeData").where("Date=`2012-02-15`", "hourOfDay(Timestamp, TZ_NY)>=11")
Note: The ticks around the timestamp are regular ticks, not backticks.
Last Updated: 16 February 2021 18:07 -04:00 UTC Deephaven v.1.20200928 (See other versions)
Deephaven Documentation Copyright 2016-2020 Deephaven Data Labs, LLC All Rights Reserved