Merging Data
Both batch and streaming data is generally put in intraday tables when imported. Once imported, merge functionality will be used on a day-to-day basis to move data from the intraday database to the historical database. It is provided by several scripts and standard classes.
Merging is normally performed for persistent data on a nightly basis. Similar to imports, merges may be performed by Persistent Query jobs ("Merge Job"), from the command line, or scripted for maximum flexibility.
Merging is closely related to Validation. After each merge operation, it is useful to verify the data quality and, optionally, delete the intraday source data.
Merge Query
When the persistent query type "Merge" is selected, the Persistent Query Configuration Editor window shows the following options:
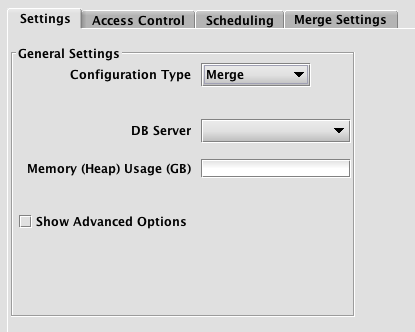
This is similar to the options presented in the previous CSVImport and JDBCImport configuration types window except for the Merge Settings tab.
Note: Merges for multi-partition imports cannot be run from a persistent query at present. This must be done from the command line.
Clicking the Merge Settings tab presents a panel with the options pertaining to merging data to a file already in Deephaven:
Merge Settings
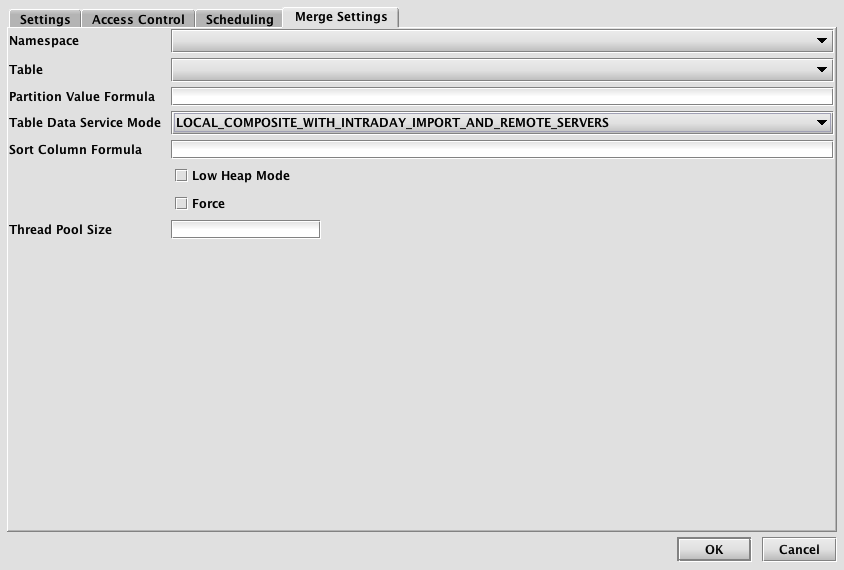
- Namespace: This is the namespace for the data being merged.
- Table: This is the table for the data being merged.
- Partition Value Formula: This is the formula needed to partition the data being merged. If a specific partition value is used it will need to be surrounded by quotes. For example:
currentDateNy()
"2017-01-01" - Table Data Service Mode: Specifies how input data to merge should be found and read. Options include:
LOCAL- Accesses all data from the file hierarchy under the Deephaven database root directory
LOCAL_COMPOSITE_WITH_INTRADAY_PROXY_SERVER- Accesses historical data in the same manner asLOCAL, but accesses intraday data via a proxy server, i.e.,db_tdcp.LOCAL_COMPOSITE_WITH_INTRADAY_REMOTE_SERVER- Accesses historical data in the same manner asLOCAL, but accesses intraday data via a remote service, i.e.,db_ltds.LOCAL_COMPOSITE_WITH_INTRADAY_IMPORT_AND REMOTE_SERVER- Accesses historical data in the same manner asLOCAL, but accesses intraday data via a composite remote service, i.e.,db_disfor same-day system intraday data,db_ltdsfor previous system intraday data, anddb_rutsfor user intraday data.LOCAL_WITH_ACTIVE_USER_LOGGER- Accesses historical data in the same manner asLOCAL, but accesses user intraday data via a remote service, i.e.,db_ruts.
- Sort Column Formula: An optional formula to sort on after applying column groupings. If no formula is supplied, data will be in source order except where reordered by grouping.
- Low Heap Mode: Whether to run in low heap usage mode, which makes trade-offs to minimize the RAM required for the merge JVM's heap, rather than maximizing throughput
- Force: Whether to allow overwrite of existing merged data
- Thread Pool Size: The number of concurrent threads to use when computing output order (i.e. grouping and sorting) or transferring data from input partitions to output partitions. More threads are not always better, especially if there is significant reordering of input data which may degrade read cache efficiency.
Once you have configured all the settings needed for your query, click the OK button in the lower right corner of the Persistent Query Configuration Editor window.
For batch data, a merge query will typically have a dependency on an import query configured in the Scheduling tab. For streamed data a merge query may simply run at a specified time.
Merge queries can also be created from an import query. After creating an import query with the Schema Editor, you will be prompted to create the corresponding merge. If you have an import query without a corresponding merge, an option to Create Merge Query will be available in the Query Config panel's context (right-click) menu.
Merge from Script
The most flexible method for merging data into Deephaven is via Groovy/Python scripting. Merge scripts may be deployed via the command line or through a RunAndDone persistent query. Merge tasks are most easily executed from a script by using a "builder" class. The underlying merge logic is identical to that accessible from the command line tools and persistent queries.
Command Line Execution
To run a script from the command line, use the iris_exec program as follows, where ./script.groovy is a local script file to execute on the server:
iris_exec run_local_script -- -s ./script.groovy -h <merge server host> -p <merge server port>
See Running Local Script for more details on options.
Note: Merging data requires the appropriate write permissions. This means these scripts should be run on a "merge server", not a "query server". Since the latter is the default in the local script runner, you must specify an alternate host and/or port to reference a merge server. See the -queryHost and -queryPort options to run_local_script.
Example
The following example shows how to execute a merge from a Groovy script. Note: there are many options not illustrated here. Please refer to Merge API Reference for all the variations available.
import com.illumon.iris.importers.util.MergeData
import com.illumon.iris.importers.ImportOutputMode
new MergeData.Builder(db,"Test","MyTable")
.setPartitionColumnValue(partition)
.build()
.run()
println "Done merging!"
This script assumes the partition is set via a command line argument and might be executed from the command line for the 2018-05-01 partition as: (Note: The port is specified to connect to the appropriate Deephaven server for merge operations.)
iris_exec run_local_script -- -s ~/myscripts/merge_single.groovy -p 30002 partition "2018-05-01"
Merge API Reference
The Merge API is fairly simple, and analogous to the Import API. There is a single MergeData class with a builder method that returns a MergeDataBuilder object. MergeDataBuilder will produce a MergeData object when build() is called. Note that this MergeData class is in the com.illumon.iris.importers.util package (there is another MergeData class in the com.illumon.iris.importers package that is not intended for use from a script). Then the merge is executed via calling the run() method on the MergeData object. is used to build the merge. The general pattern for performing a merge is:
MergeData.Builder(db,<namespace>,<table>)
.set<param>(<param value>)
...
.build()
.run()
Merge Options
|
Option Setter |
Type |
Req? |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
setPartitionColumnValue |
String |
No* |
N/A |
A literal string used to select the column partition to merge. Often a date, e.g.. " |
|
setPartitionColumnFormula |
String |
No* |
N/A |
An expression that will be evaluated to specify the partition to merge. For example |
|
setThreadPoolSize |
int |
No |
4 |
The maximum number of parallel threads to use during the merge process |
|
setLowHeapUsage |
boolean |
No |
false |
Whether to prioritize heap conservation over throughput |
|
setForce |
boolean |
No |
false |
Whether to force merge when destination(s) already have data |
|
setAllowEmptyInput |
boolean |
No |
true |
Whether to allow merge to proceed if the input data is empty |
|
setSortColumnFormula |
String |
No |
N/A |
Formula to apply for sorting, post-grouping. For example, to sort on Timestamp, binned by second: |
* Either a partition column value or formula must be specified (not both).
Data Merging Classes
Note: It is recommended that merges should be executed by Persistent Query jobs or by scripting, not by directly calling these classes. This information is provided primarily for administrators who want an in-depth understanding of the merge processing.
The MergeIntradayData class is used to copy and reorganize data from intraday to historical storage.
This class is primarily used by merge queries created in the Query Configuration Editor or by the Schema Editor in the Deephaven UI. However, it can also be used by the XML-driven import and merge scripts. Merge queries are the preferred method to use the MergeIntradayData class, but it can also be called directly, used from custom scripts, or called from an application. This section details its functionality and arguments.
Intraday data is written into column files in the order in which it arrives. As such, there is no grouping of data, and the only sorting is by arrival time of the events. Since intraday data is typically used for data that is still receiving updates, the main priorities are around low latency in appending to the table and delivering those updates to running queries. Historical data does not receive updates, so the priority there is around organizing data for more efficient querying.
Functionality of the MergeIntradayData class
The MergeIntradayData class reads intraday data for a specified partition (usually a date) and writes it into historical storage. During this process, the class can group the data based on grouping columns specified in the schema, sort data based on an argument passed to the class and distribute data across one or more writable partitions.
Note: These writable partitions are different from the column partition indicated by the partitioning column in the schema. Writable partitions are storage partitions set up to allow sharding of historical data for faster querying and potentially to provide for larger total storage capacity. See: Historical Partitioning.
When sharing data, the MergeIntradayData class uses the partitioning keyFormula defined in the table's schema. This formula describes how data should be distributed when there are multiple writable partitions configured for historical storage. For more details see Schemas.
In addition to the MergeIntradayData class, there is also a RemergeData class. It provides similar functionality, but merges data from existing historical partitions for one namespace and table into new historical partitions for a different namespace and/or table.
During merge processing, the source data is read, and a Deephaven byExternal method is used to create a new sub-table of results for each partition based on the target table's partitioning formula. Then, for each partition sub-table, groups are aggregated and ordered from largest to smallest (number of rows in the group). Optional sorting is applied to rows within the groups, and the grouped data is then written out to disk. Note that columns used for grouping cannot be used for sorting.
Arguments and Property Settings
The MergeIntradayData class (com.illumon.iris.importers.MergeIntradayData) main takes the following arguments:
Required (first three arguments, in this order):
<namespace> <tableName> <partitioning column value>
Optional (by name, after the three required arguments):
sortColumn=<column name or formula to sort by>
tableDef=<absolute path to table definition file>
lowHeapUsageMode=<true or false>
force=<true or false>
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
namespace |
(required) Namespace in which to find the table whose data is to be merged. |
|
tableName |
(required) Name of the table whose data is to be merged. |
|
partitioning column value |
(required) This is typically a date string but could be some other unique string value. It indicates what column partition will be merged by this merge operation. |
|
sortColumn |
(optional) A formula by which to sort rows within a group. If not provided, rows within a group will be sorted based on the order in which they were written into the intraday partition. This column cannot be one of the grouping columns. |
|
tableDef |
(optional) If a different table definition is to be used for the merge operation, or the table definition is not accessible within the context in which the merge operation is being run, this value can provide a path to the definition file. |
|
lowHeapUsage |
(optional) Reduces memory consumption of the merge process at the expense of throughput. Restricts most activities to single-threaded, one-by-one, and limits expansion of indexes in memory. |
|
force |
(optional) By default, a merge will fail if any historical partition already exists for the data to be merged. Force will cause merge to overwrite the existing destination(s). |
The RemergeData class (com.illumon.iris.importers.RemergeData) main takes the following arguments:
Required (first five arguments, in this order):
<sourceNamespace> <sourceTableName> <namespace> <tableName> <partitioning column value>
Optional (by name, after the five required arguments):
sortColumn=<column name or formula to sort by>
tableDef=<absolute path to table definition file>
lowHeapUsageMode=<true or false>
force=<true or false>
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
sourceNamespace |
(required) Namespace in which to find the table whose data is to be re-merged. |
|
sourceTableName |
(required) Name of the table whose data is to be re-merged. |
|
namespace |
(required) Namespace in which to find the table into which to re-merge the data. |
|
tableName |
(required) Name of the table into which to re-merge the data. |
|
partitioning column value |
(required) This is typically a date string but could be some other unique string value. It indicates what column partition will be merged by this merge operation. |
|
sortColumn |
(optional) A formula by which to sort rows within a group. If not provided, rows within a group will be sorted based on the order in which they were written into the intraday partition. This column cannot be one of the grouping columns. |
|
tableDef |
(optional) If a different table definition is to be used for the merge operation, or the table definition is not accessible within the context in which the merge operation is being run, this value can provide a path to the definition file. |
|
lowHeapUsageMode |
(optional) Reduces memory consumption of the merge process at the expense of throughput. Restricts most activities to single-threaded, one-by-one, and limits expansion of indexes in memory. |
|
force |
(optional) By default, a merge will fail if any historical partition already exists for the data to be merged. Force will cause merge to overwrite the existing destination(s). |
In addition to these arguments, both classes will use the property iris.concurrentWriteThreads to control parallelization of processing, executing steps that allow for parallel processing via a thread pool whose maximum capacity nConcurrentThreads is defined by the value of that property.
The initial execution of byExternal, to partition the results, is single threaded. Subsequent steps may be parallelized depending on nConcurrentThreads, the value of lowHeapUsageMode, and the number of destination partitions.
For each destination partition, the output ordering must be determined by grouping and sorting the input data that will be written to that partition. Following this, the data must be written according to said ordering.
In lowHeapUsageMode, only one destination partition is processed at a time. For each partition, the ordering is determined in a single thread, and then the thread pool is used to execute writing jobs for each column of the output table.
Otherwise (if lowHeapUsageMode is false), all destination partitions are processed in parallel, to the limit imposed by nConcurrentThreads. The ordering jobs for the destination partitions are executed via the thread pool, as are the writing jobs for each output column of each destination partition.
Minimum heap usage for the merge process would be with iris.concurrentWriteThreads = 1 and lowHeapUsageMode = true. The other extreme of tuning would be lowHeapUsageMode = false and concurrentWriteThreads set high enough that all output partitions and column writes could be processes in parallel. This "maximum throughput" configuration can easily consume large amounts of memory and dominate I/O channels. Configurations that move towards maximum throughput should be evaluated carefully.
Last Updated: 23 September 2019 12:19 -04:00 UTC Deephaven v.1.20181212 (See other versions)
Deephaven Documentation Copyright 2016-2019 Deephaven Data Labs, LLC All Rights Reserved